When I finished Jamuary I was resigned to taking time off before patching again. Jamuary was exhausting, and I’m tired. I wasn’t sure how long it might be before I patched again. It turns out the answer was “immediately.” By 10pm on February 1st I was bored, and so decided to put something together on the iPad for fun. I had no intention to record it. I was just playing around with a few things to see how they work. The same thing happened on the 2nd. I started to watch a YouTube video, and decided that I’d rather just do a patch on the synth that was sitting not eight feet from me than watch someone else do one. And so I did.
I knew from the start I wanted it to be in a minimalist vein. Maybe not the dictionary definition of Minimalism as a musical discipline, but still something with not much going on. You know; minimalist.
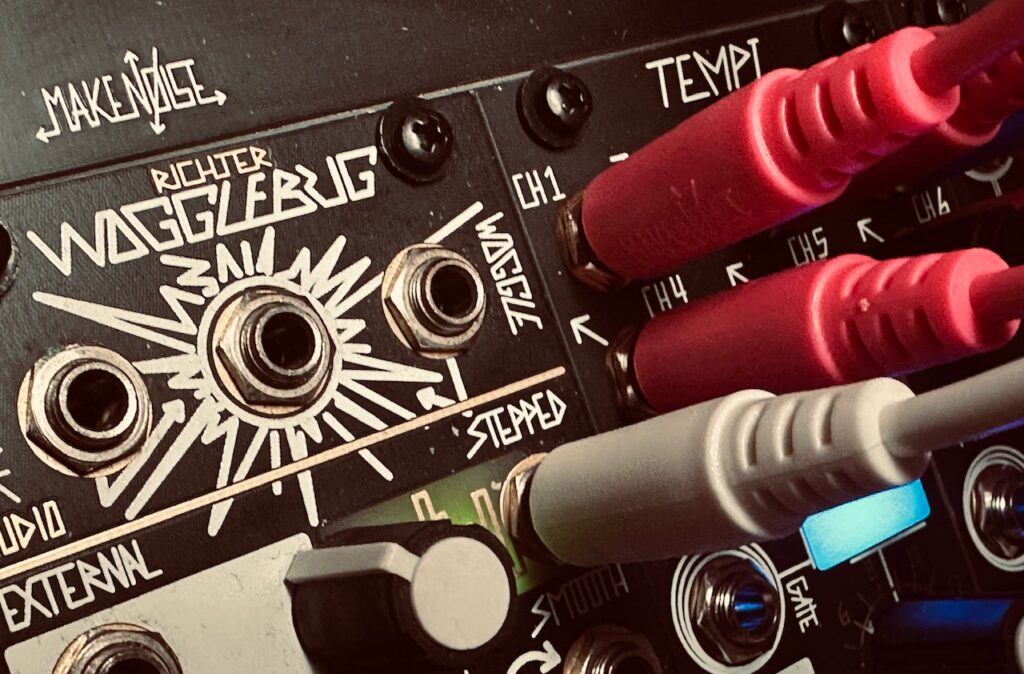
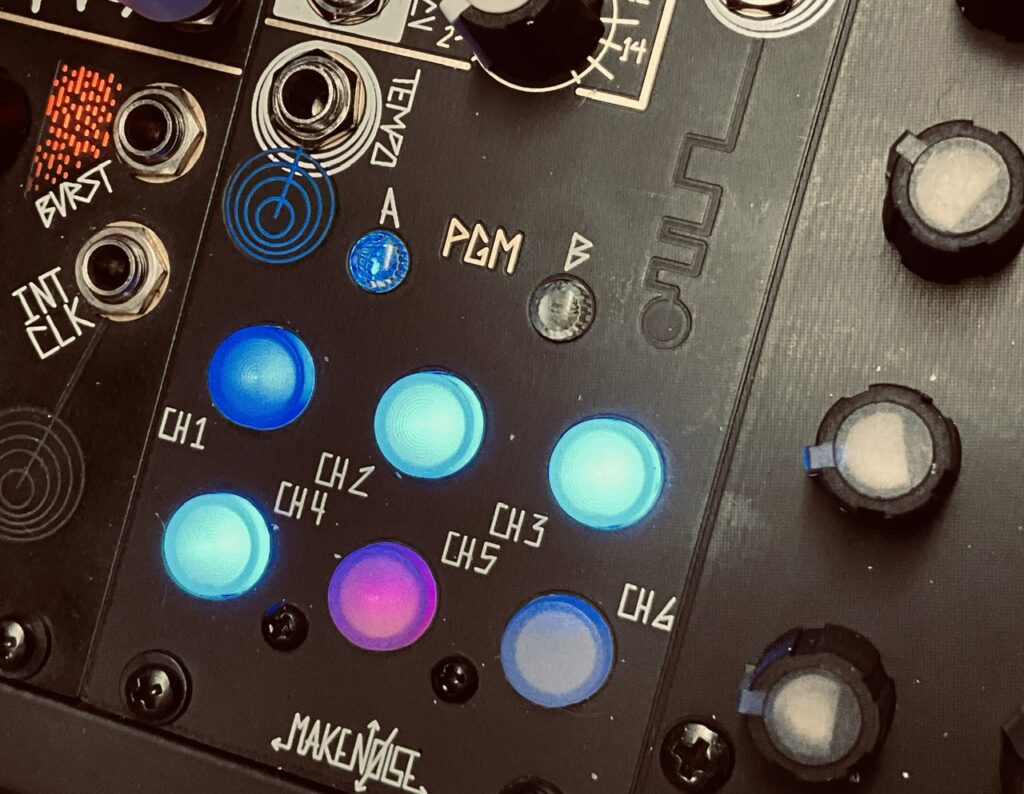
The patch started with Tempi. The base tempo was ~60bpm:
- Channel 1 (x1) > Mimeophon
- Channel 2 (x1) > René X Clock
- Channel 3 (x2) > René Y Clock
- Channel 5 (/5) > René X Mod
- Channel 6 (/7) > René Y Mod
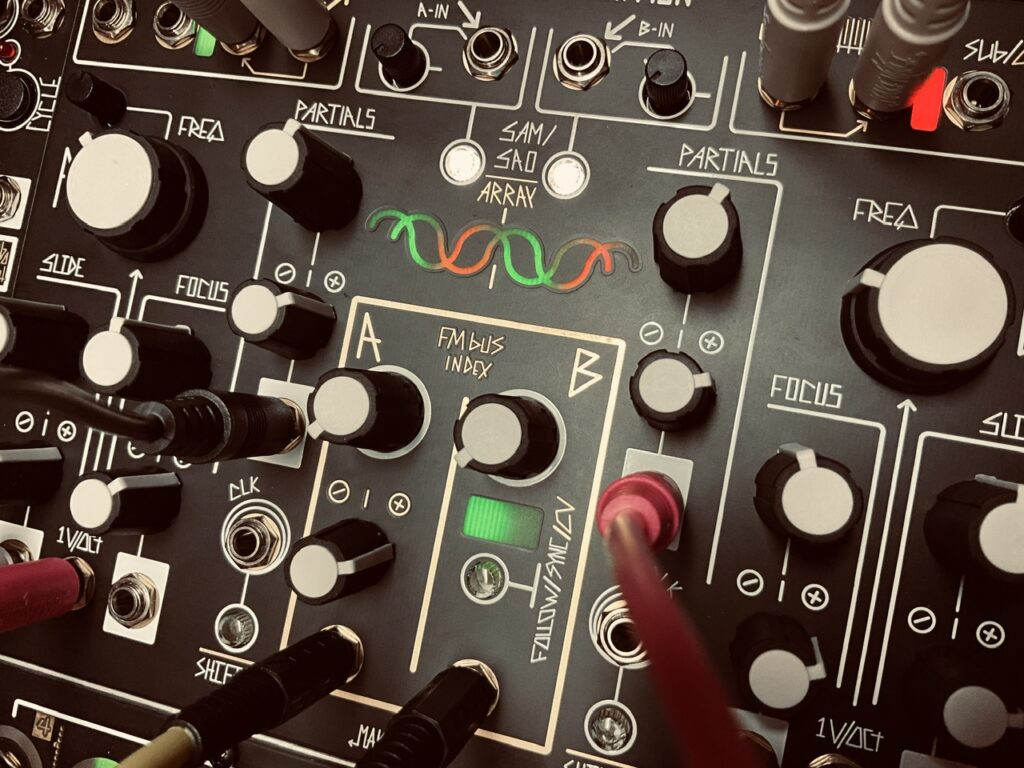
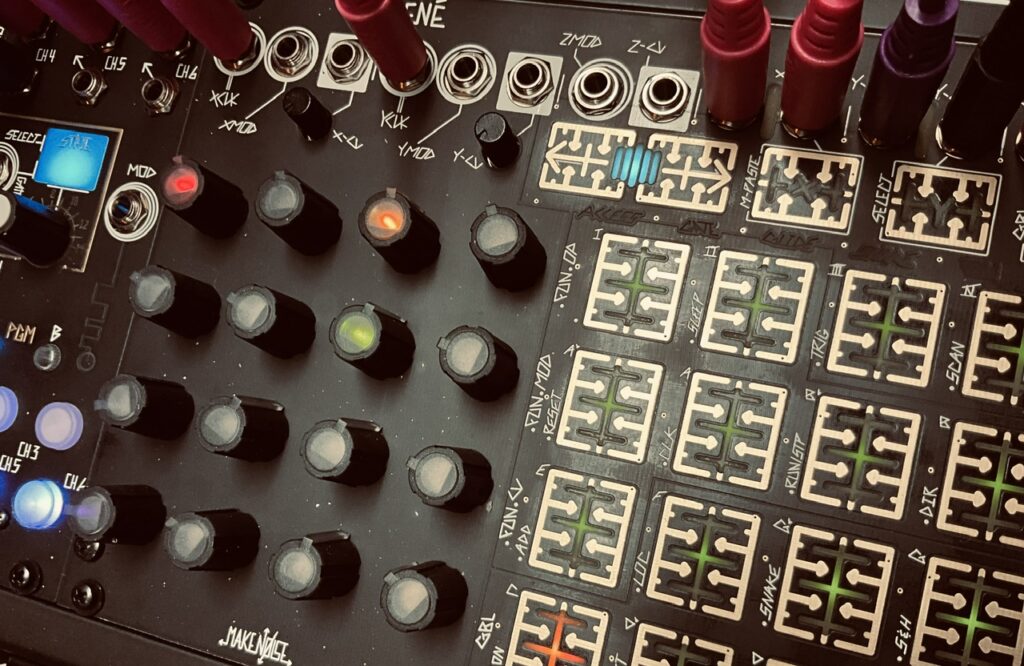
René received the clocks and Mod gates from Tempi on both the X and Y channels. Mod on both channels was set to Start/Stop on the Fun page. When the gate is low at their respective Mod inputs, the sequence moves forward, when it’s high, it stops. Since all four clocks are at different times, there is no continuous repeating pattern, each channel starting and stopping every bar and change. Gates and Access were adjusted for both channels throughout the performance to guard against becoming stagnant. René controlled all four voices in the patch, using just two oscillators, Spectraphon and STO. As far as I know, the scale is in C Lydian, but it sounds like I may have neglected to make the key change between C Major and C Lydian in one (or more 😬) of the channels. It doesn’t happen often, but we get a hint of dissonance on occasion.
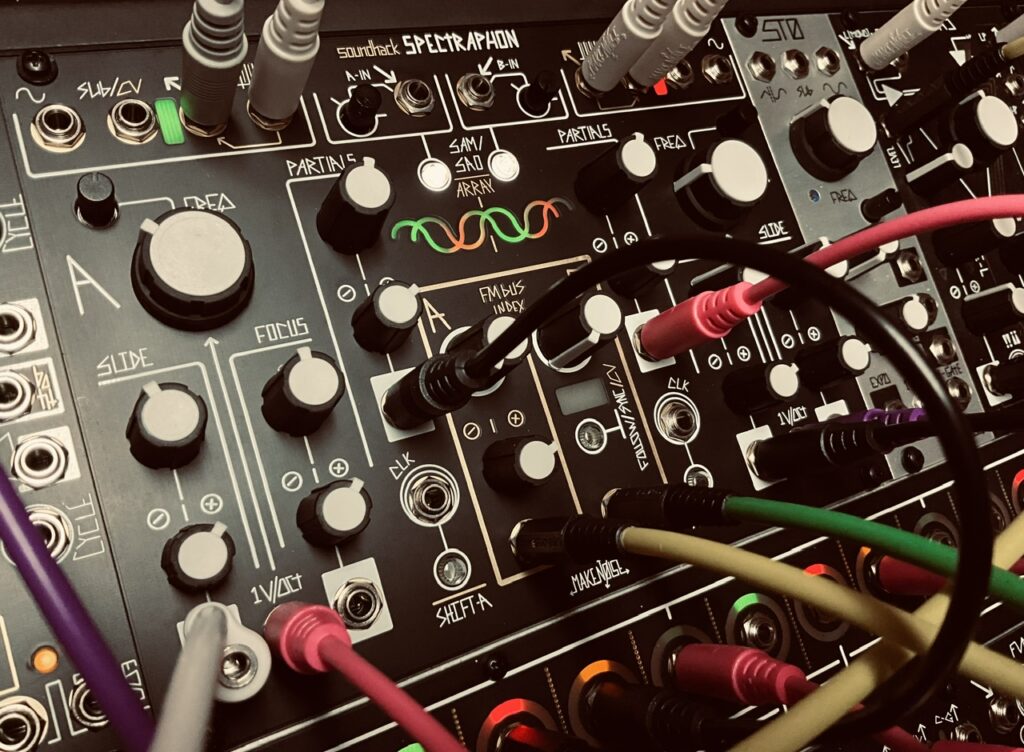
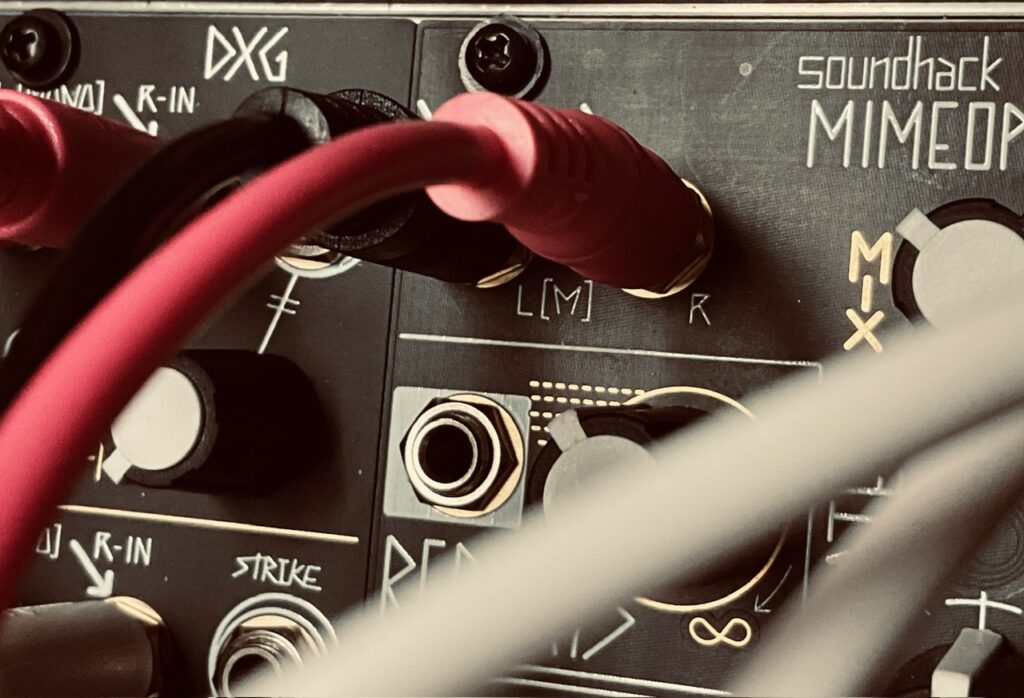
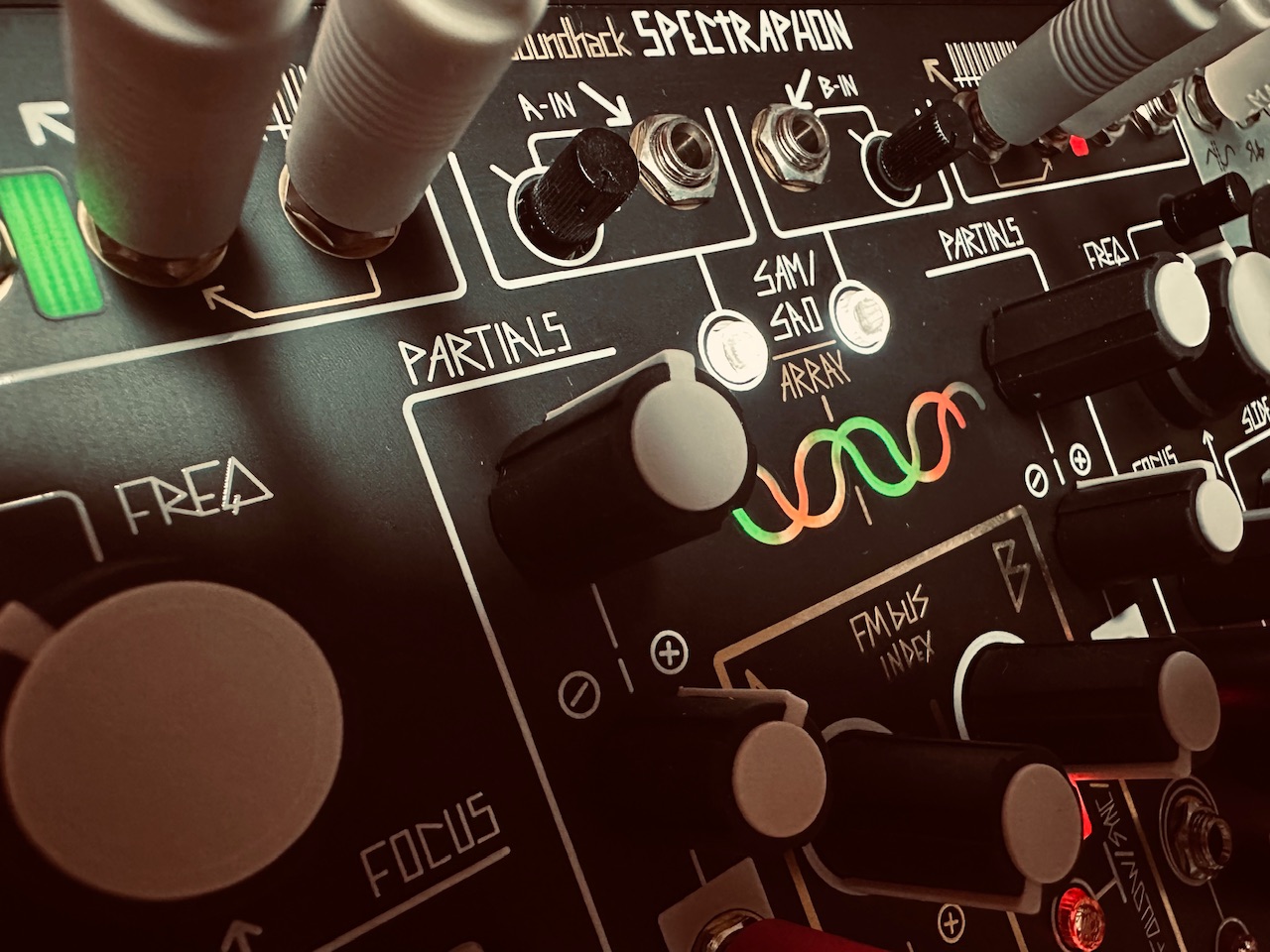
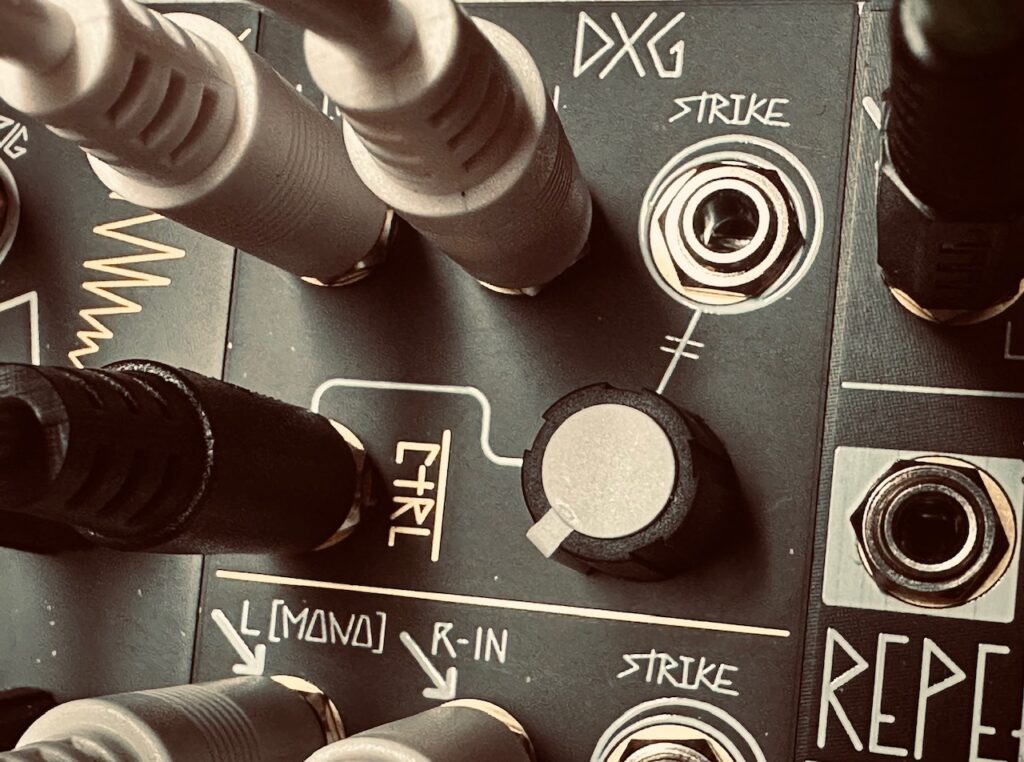
The X Channel sent pitch CV to Spectraphon’s A side, and the trigger from the X Gate output to DXG’s Channel 1 Strike input. The Y channel was routed similarly to Spectraphon’s B side and DXG’s Channel 2 respectively. These two oscillators form the first voice, comprised of fairly sparse pings in the DXG. The mixed outputs from Spectraphon A and B were sent to DXG in a way to remain discrete left and right with their separate gate patterns. When you plug something into the Left input on any DXG channel, it normalizes to the Right channel and becomes a mono signal at the output. In order for the Left (mono) input to remain in the left channel only, a dummy cable should be plugged into the Right input. This dummy cable breaks the normalization, and will send audio at the Left channel input to only the Left channel at the output. I plugged Spectraphon’s A side Mix output into DXG’s Left input on Channel 1, along with a dummy cable in the Right input. Spectraphon’s B side Mix output went to DXG’s Right input on Channel 2. This kept the A side pings on the left side of the stereo field, and the B side pings on the right for a delightfully stereo experience of pings and echoes.
Both sides of Spectraphon were tuned to C one octave apart. Spectraphon was modulated in three places, but only moderately. The A Side Focus and Slide were modulated by a Maths envelope and Wogglebug’s Stepped outputs respectively. The B Side Slide was modulated by the Maths OR output. The slight modulation helped to have subtle timbre changes on the pinged notes, some brighter and others darker. Both sides also FM’d each other slightly. The FM Bus Index for both channels were around 8:30 on the knobs. There’s some FM, but not very much at all. Just enough to give notes a kind of bounciness once struck in the LPG. One really nice feature of the Spectraphon’s FM capability is that its sine waves always stay pure in order to avoid the problems associated with cross-modulating oscillators. No matter how much one might FM Side A, its sine wave can still modulate the B side with a clean sine wave rather than one that is FM’d. Most oscillators, once they become carriers, are useless as modulators. Not so with Spectraphon where both oscillators can be both modulator and carrier oscillators at the same time. Very nifty.
René’s Cartesian Channel performed an identical role with STO and QMMG as the X and Y channels with Spectraphon and DXG. I wanted something well above the predominant audio register in the patch. High pitched tings and drips, in the same manner as the Spectraphon pings, only even more sparse. These were designed to be ornamental notes, not the star. The Cartesian Channel CV output sent pitch CV to STO’s v/oct input, and its trigger output went to Channel 2 of QMMG for similar pinging with the Cartesian trigger. The STO’s sine output was used to keep the notes with as soft a texture as I could with pings. One interesting difference between using the QMMG and DXG as a LPG is that QMMG’s decay, at least my QMMG’s decay,1 is noticeably longer on higher pitched notes than the DXG when pinged with a trigger. In the DXG, higher pitched notes are sometimes just barely blips. This sort of behavior is generally expected with just about every LPG because of how they filter the upper harmonics. But through the QMMG, those high notes are seemingly longer. It’s certainly a result of the those juicy QMMG vactrols, and a good argument for keeping vactrol LPGs around, cadmium eaters be damned. These pings in the QMMG were mixed in with the Spectraphon A and B side pings via the Aux input in the DXG.
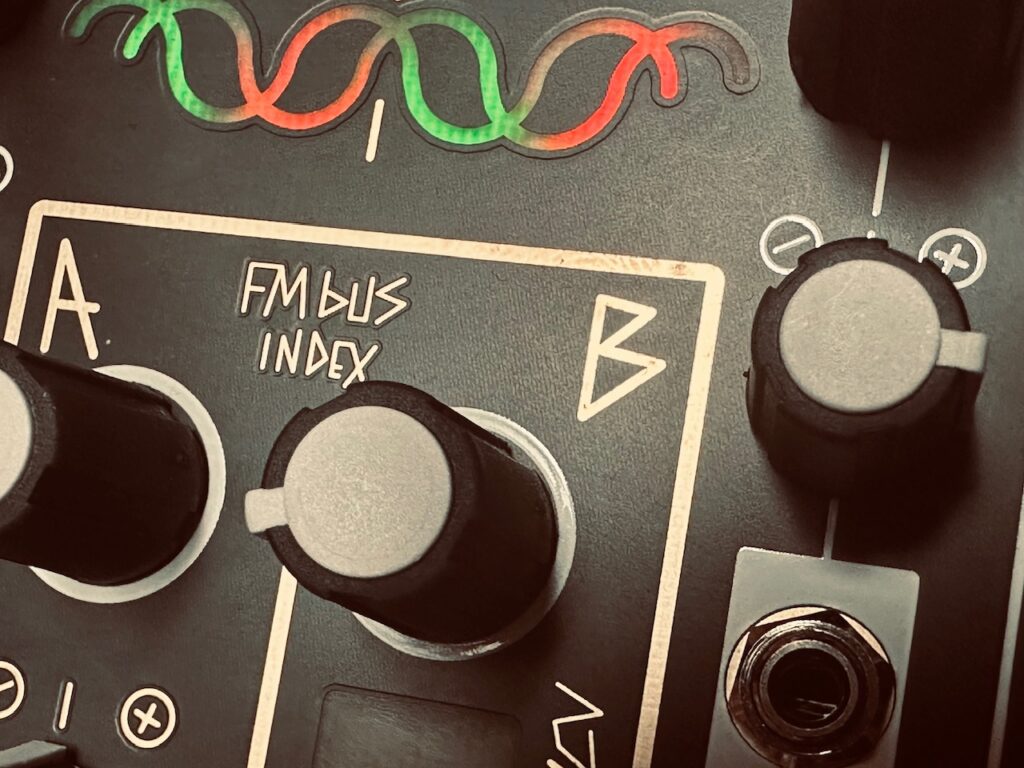





After I worked up the pinging I was after, I knew I wanted something more, but it had to be complementary and juxtapose itself against the very delicate pings. I was in a stream of consciousness-like trance when building this patch, and so even though I’ve documented all of the final patch connections for the entire patch, I’m not exactly sure what thought process led me to how I was going to fill in the space in a graceful way. A bit of experimentation, some clever routing, and tinkering seemed to be the answer.
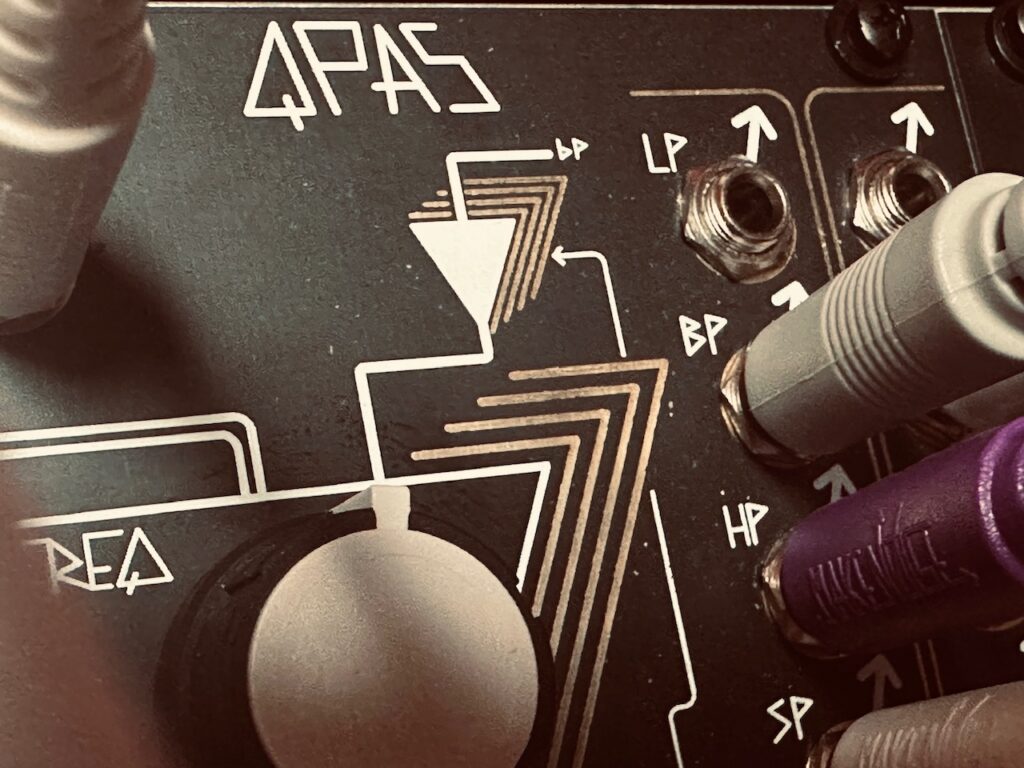
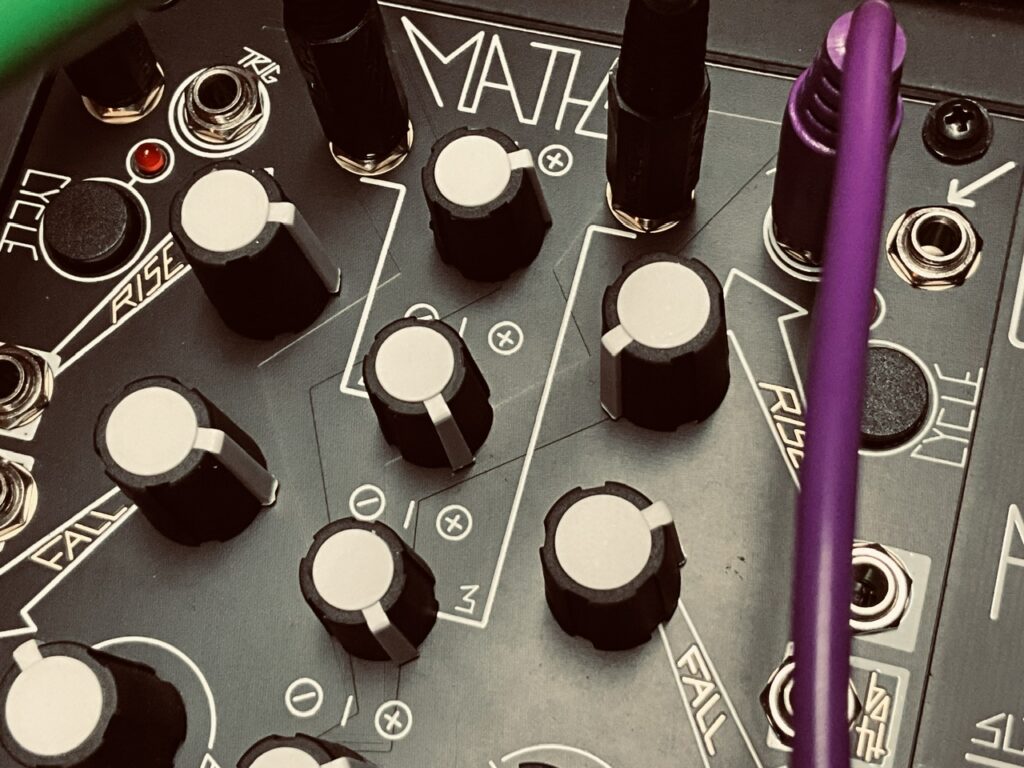
I first decided I wanted to use QPAS. I’m not sure how I decided on it being heavy filtering, but I knew I needed the voice to be subtle so as not to overtake light pinging happening in the stereo field. I sent Spectraphon’s A side Sine wave to the L input on QPAS, and the B side Sub output to QPAS’s Right input. The trick was to have both oscillators filtered by QPAS, yet remain separate in the outputs. QPAS essentially became a dual mono filter with shared controls.2 The frequency knob on QPAS, for most of the performance, was moderately low, around 10 o’clock on the knob, though it was being modulated by an unsync’d Wogglebug’s Smooth output, while both Radiate knobs were being modulated by the Woggle output.
QPAS’ Left and Right outputs would become completely separate voices, unfettered by any gating or enveloping, being tamed and shaped only by the filter cutoff(s) and resonance(s) before going straight to the output. Because these outputs weren’t being gated or enveloped, they were always present, moving along with their respective pitch sequences from René, Spectraphon’s A side following the X Channel, and the B side following the Y channel. I remember really liking the sound of the voices and the feel they added, but struggled to find a solution to these sequences droning along overtaking the pings. The answer was simple: only send as much volume to QPAS’ inputs as is absolutely necessary, and allow the resonance to do some of the lifting. It’s a delicate balance between not being audible and drowning out everything else; the output needed to be always present, but delicate enough to not use all of the space in the sonic field.


The Right Low Pass and Smile Pass outputs went straight to X-Pan Channel 2 A and B inputs where they were crossfaded and slowly panned across the stereo field (by the same cycling envelope). This melody carried a mostly present sequence from the Y channel, though quite muffled by the filter and constantly swirling with the crossfading, and smoothed out with resonance, then copious amounts of Mimeophon with Halo. From the time it was introduced, this Y melody is omnipresent, filtered to various degrees, and allowed to drift through the stereo field.
The Left outputs is where the routing became a bit of voodoo. I know what connections led to this sound, but I’m not sure I understand the mechanisms that led to the result. It was a sine wave playing a sequence heavily filtered by QPAS,3 and then very heavily filtered again by QMMG. The Left Low Pass and Smile Pass outputs were routed first to QMMG channels 3 and 4. I tried all four modes, but only the Low Pass mode gave me the specter of a ghost lightly singing in the background, occasionally wavering and trembling as the pitch of the input, slowly moving filter cutoff, and resonance interacted with one another. When the voice was introduced, the filter on QMMG was completely closed, only being modulated by a cycling Maths envelope. Resonance started at about 8:30 on each knob. I slowly added more resonance, then more again, before also slowly raising the cutoff. By the time I hit stop on the recording, both the cutoff and resonance for both channels were at about 1 o’clock on the knobs. It sounds as if it’s a feedback patch, though, outside of the copious amounts of resonance in the QPAS and QMMG signal paths, tamed by the controlled input into QPAS, there is no feedback patching.4 These two outputs from QMMG were crossfaded in X-Pan, so that the sound constantly drifted and resonated in interesting ways. This led to wavering cries that occasionally had a smidge of growl enough to resonate through the Mimeophon in an incredibly beautiful way.




This voice, although the most subtle and delicate, as well as the least present, is by far my favorite part of this patch. It brings the patch to life. It’s one of the coolest sounds I’ve gotten from any patch. When I first heard that sound I stood tall and stared straight at the QMMG as if to ask it to teach me its wizardry. It was the first time I’ve looked at the QMMG as an instrument; as something more than a set VCAs, LPGs, and filters, with a mix output.
All four voices were mixed in the X-Pan, and sent to the Mimeophon for some delay-ification and Halo, the soft noise of the Mimeophon cushioning the edges in subtle ways.
Like so many patches I made during Jamuary, this patch is an open testament to a cohesive Make Noise system being a fluid instrument. It’s an absolute pleasure to play.
One small issue I had, which reinforces my desire for a couple of VCAs than can boost levels before going to the ES-9, was that the recording was ultra-quiet. The pings are very quiet, which necessitated a low volume for everything else in the patch. I needed to add a full 12.5dB in post in order to bring my peaks up to ~ -12dB in AUM.


Modules Used:
Tempi
René Mk2
Spectraphon
STO
QPAS
QMMG
DXG
X-Pan
Maths
Function
Wogglebug
Mimeophon
Improvised and recorded in one take on iPad in AUM via the Expert Sleepers ES-9.
- Each QMMG will have a different response because of the natural variability of vactrols. Make Noise does a great job of matching vactrols in an individual unit as closely as possible, but there are (sometimes noticeable) differences in the decay length between different units. This is the same for all vactrol-based LPGs. ↩︎
- Definitely a first time using QPAS in this way. ↩︎
- Filtering a sine wave is about as pedestrian a job as a filter can do. It’s normally unremarkable as filters thrive on upper harmonics. ↩︎
- If the input level was much louder, I’m confident the resonance, particularly in QMMG, would have been screaming. Both filters have a very pronounced resonance that can run away quickly. ↩︎