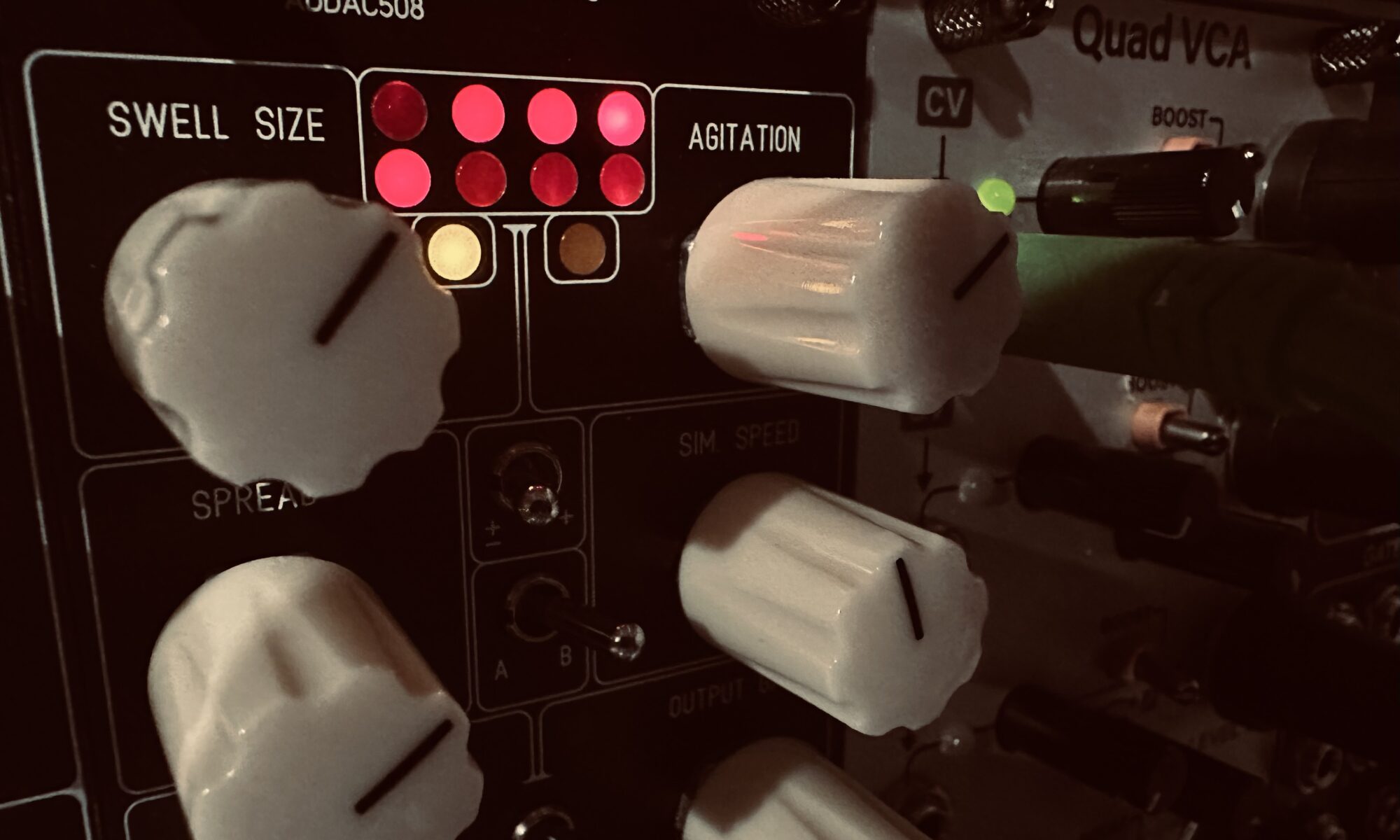
Today I decided to go back to a technique I’ve rarely used, and on a much grander scale. I don’t use noise very often, and when I do it tends to be for the obvious use cases. Hit hats, wind and ocean sounds, sprays, etc. I seldomly use it for modulation, and only once have I used noise of any flavor to amplitude modulate an oscillators wave. Today I would do it again, times eight.
I conceived of using noise to modulate all eight harmonics of the Verbos Harmonic Oscillator this morning as my wife was talking to me. I even popped up a bit at the idea, and she took notice.
Wife: “What?”
Me: “Nothing. Just had a thought occur to me. Not even sure if it’s worth a shit.”
I spent the better part of the morning and early afternoon thinking about how I wanted to do this patch. I knew that just noise into each harmonic’s VCA wasn’t it. Then it occurred to me: Chaos! As soon as this though hit my brain I knew what to do, and immediately went to the synth to start patching.
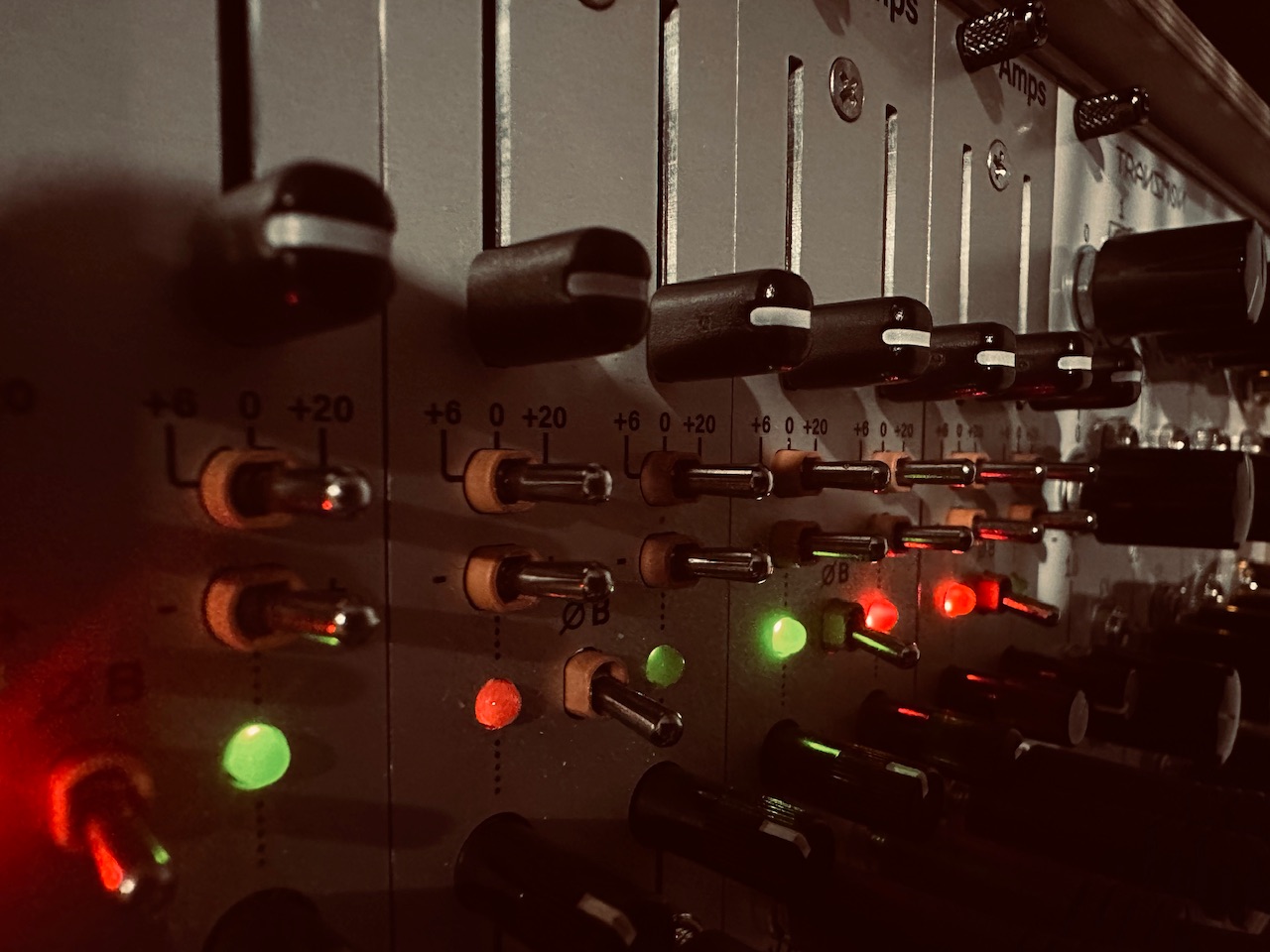
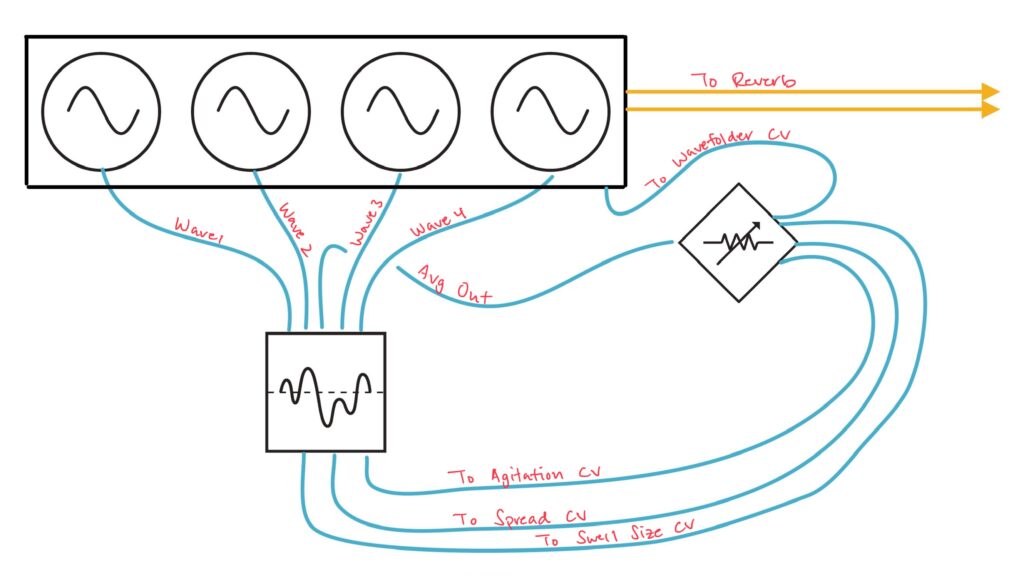
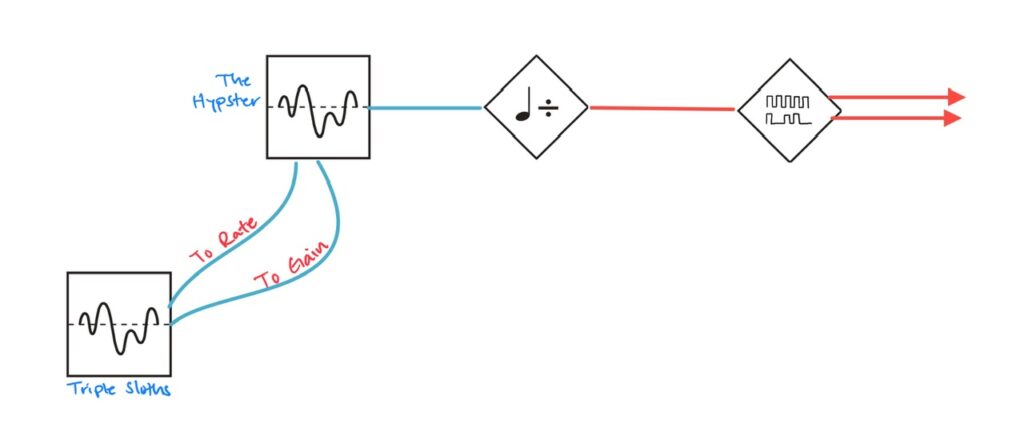
I ran blue noise from Sapel to input 1 of the Intellijel Amps. Amps is a special sort of VCA. Everything cascades. All inputs cascade, as do CV inputs, and there are mixing outputs as well. It’s incredibly flexible. I have four of them chained together to be an eight channel “super VCA/submixer” and it’s been a great choice. Since each input cascades, I only needed one noise input to run this entire section of the patch. Every other channel received that same blue noise input as well. Into each channel’s CV input I patched one of the eight outputs from Nonlinearcircuits The Hypster to chaotically modulate the noise levels of all eight channels independently. Once that was patched, I ran each Amps output to its own Harmonic Oscillator VCA input at random. The only part of this patch that was planned were the first and fifth harmonics, which received their noise modulation from the U and -U outputs on The Hypster as they’re the outputs with the highest amplitude. Each harmonic was slowly brought in by slowly adjusting each CV attenuator individually at random until they were all playing. The nature of chaos means that cycles, even if semi-regular at times, don’t repeat exactly the same, and the harmonics never played the same twice, which kept movement interesting. There were often pauses or redirections in motion for each harmonic. Wonderful.
The mixed HO output was patched to the Multi-Delay Processor. I’ve been taken in by the earthy sound of the Harmonic Oscillator. Each harmonic sine wave has a little hair on it once you give them a little push. The drive in the MultixDelay Processor, both on the input and on each tap output, accentuates that hair in all the right ways. This Verbos ecosystem is warm and inviting, but it can also roar. Taps four and eight were patched to the Verbos Scan & Pan, hard panned left and right, and the output of the MDP, which only had the dry signal, was patched to be in the middle of the mix. This mix created a strong signal with some subtle stereo movement which ended up being fantastic. This stereo signal was then patched to the stereo matrix mixer to be spread around to different effects.
The Rossum Panharmonium fed the Holocene Electronics Non-Linear Memory Machine, which was set with a fairly slow delay and full clockwise smearing, which really smoothed out the Panharmonium’s output for an accompanying drone that floats along beside the ever moving Harmonic Oscillator. This output then fed the Dradd(s), which did its thing in Grain Mode (although I think I forgot to turn on the modulation to both P1 and P2 on both Dradds 😬 – I’m also not convinced it isn’t lost in the mix).
I’m very pleased with how this patch turned out and was a great success at using this technique which I’ll be sure to use more often.
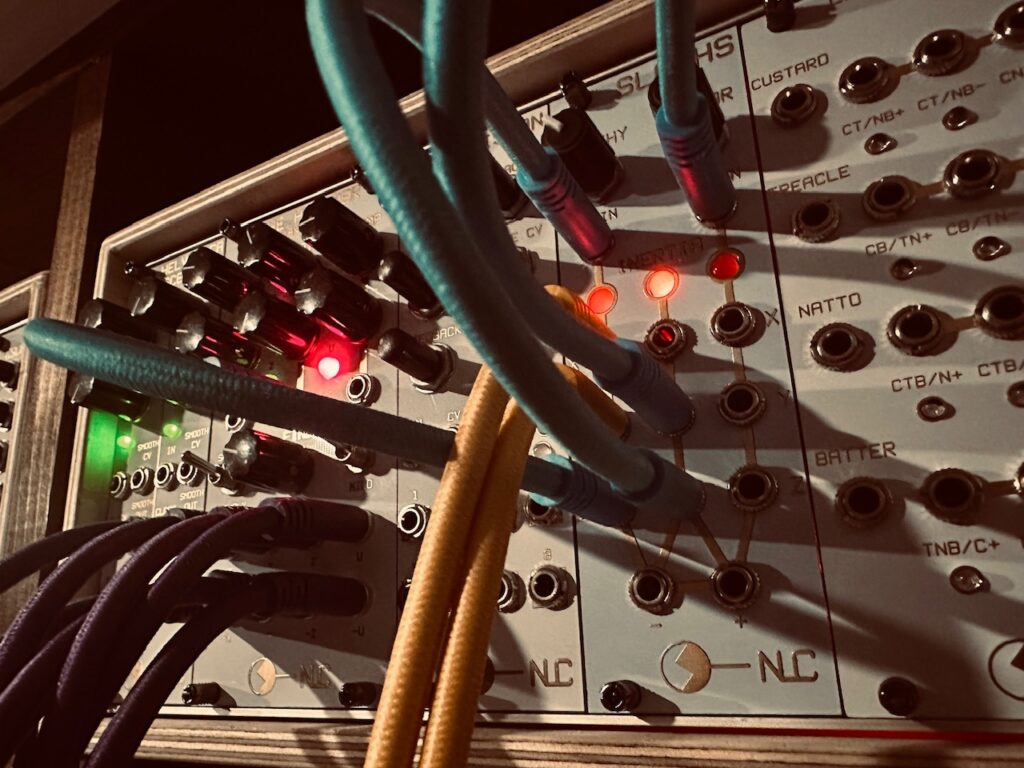
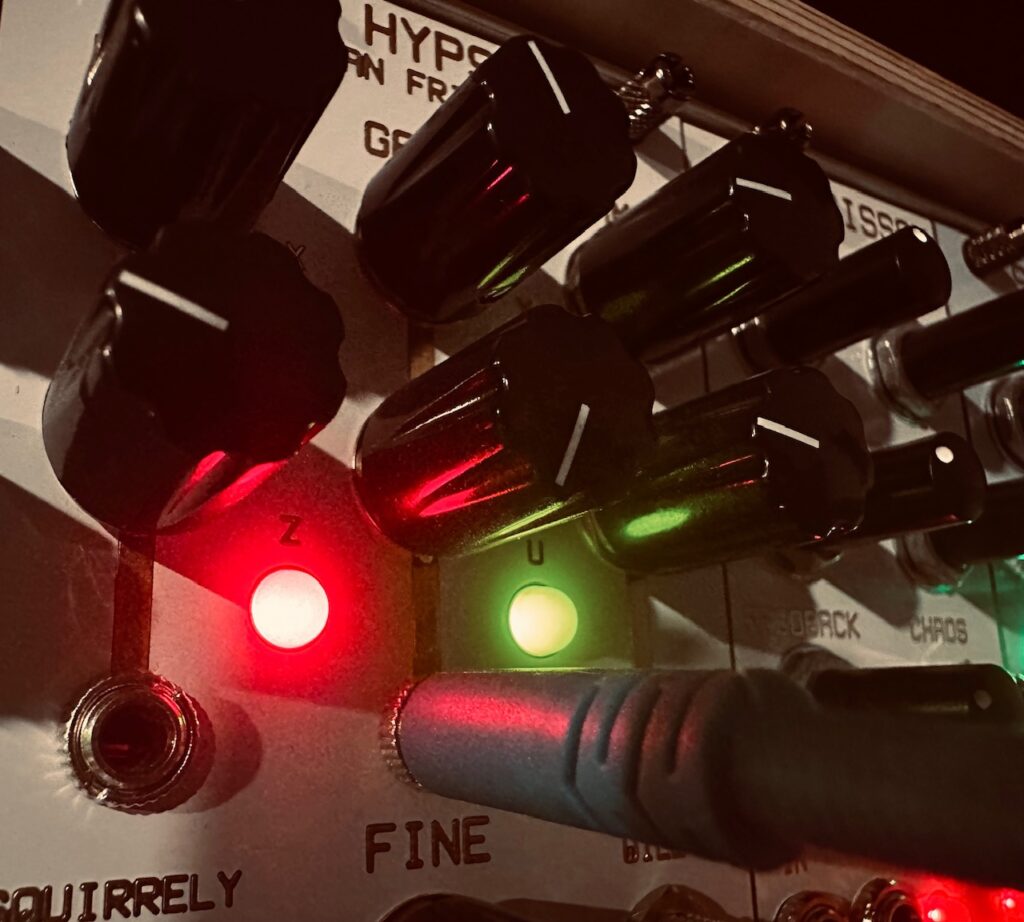





Modules Used:
Nonlinearcircuits The Hypster
Nonlinearcircuits Triple Sloths
Intellijel Amps
Frap Tools Sapel
Verbos Harmonic Oscillator
Verbos Multi-Delay Processor
Verbos Scan & Pan
AI Synthesis 018 Stereo Matrix Mixer
Rossum Electro-Music Panharmonium
Holocene Electronics Non-Linear Memory Machine
Pladask Elektrisk Dradd(s)
Knob Farm Ferry
Outboard Gear Used:
Walrus Audio Slöer
Plugins Used:
Toneboosters TB Equalizer
Performed and recorded in 1 take in AUM on iPad via the Expert Sleepers ES-9.