It had been a couple of weeks since I’ve been able to patch, and I was itching. Having just been on a spring break high school baseball trip to the beautiful Emerald Coast, I was inspired by the sea. It was the first trip in over a year I hadn’t taken some music making device, and even if I didn’t really have the time to patch during this trip, I missed not having something.1 I thought all week about what I would be making if I had my synth, and Swell Physics was first and foremost in those musings.
When I first set up this patch it was a mess. A cacophony of sound where each part seemed to work well on its own, but as soon as it mixed with other parts the whole thing turned to shit. As a non-professional musician, I try not to fall into that trap of being too hard on myself when my results are less than what I’d hoped for. Failure, after all, is the key to progress and improvement, and if a recording sucks it’ll just go into the folder of dozens of other recordings that suck. My livelihood is not at stake, and I don’t yet have a reputation to ruin. When I turned on my synth today, I listened to that latest patch still plugged in, and I was unhappy. It was a mess, and only reminded me that the recording I had heard of that patch a dozen or more times that week just wasn’t it. I was resigned to tearing the patch down and starting from scratch, but since I wanted to use the same control scheme I instead chose first to tweak a few settings and see if I couldn’t salvage the patch.
I don’t really like tweaking already-built patches. I mean, I like tweaking controls, but not patch points. It’s generally not been an exercise that has produced meaningful fruit, and I usually find it easier to simply start over rather than navigate a nest of patch cables. Today’s first change, however, wasn’t a physical patch change, but a setting change to the E370. Rather than using one of the User wavetables I’ve taken fancy to, a very cool wavetable leftover from the previous owner, I switched all four channels over to ROM A, and the difference was immediate. In fact, it was pretty much the sound I envisioned before i even started patching. So much for tearing down the patch.
The patch starts, as many of my patches often do these days, with the Addac System Addac508 Swell Physics. Since first receiving Swell Physics many of my favorite recordings are based around it. Whether I’m using the wave outputs directly to control levels, or in conjunction with modules like the Nonlinearcircuits Numberwang and Let’s Splosh to control various facets of a patch, I’m constantly finding new ways to integrate it into my work. The four outputs were sent to an array of Intellijel Amps’ CV inputs to control the levels of four modulated outputs from the always lovely Synthesis Technology E370 quad wavetable oscillators and blue noise to simulate the spray of the ocean. Each oscillator was fed pitch information from the NOH-Modular Pianist, one note each of a D minor seventh chord (though I’ve no idea what the oscillator was tuned to). From the Amps, the mixed noise and audio outputs went to the ST Modular Sum Mix & Pan to place in the stereo field of the mix.

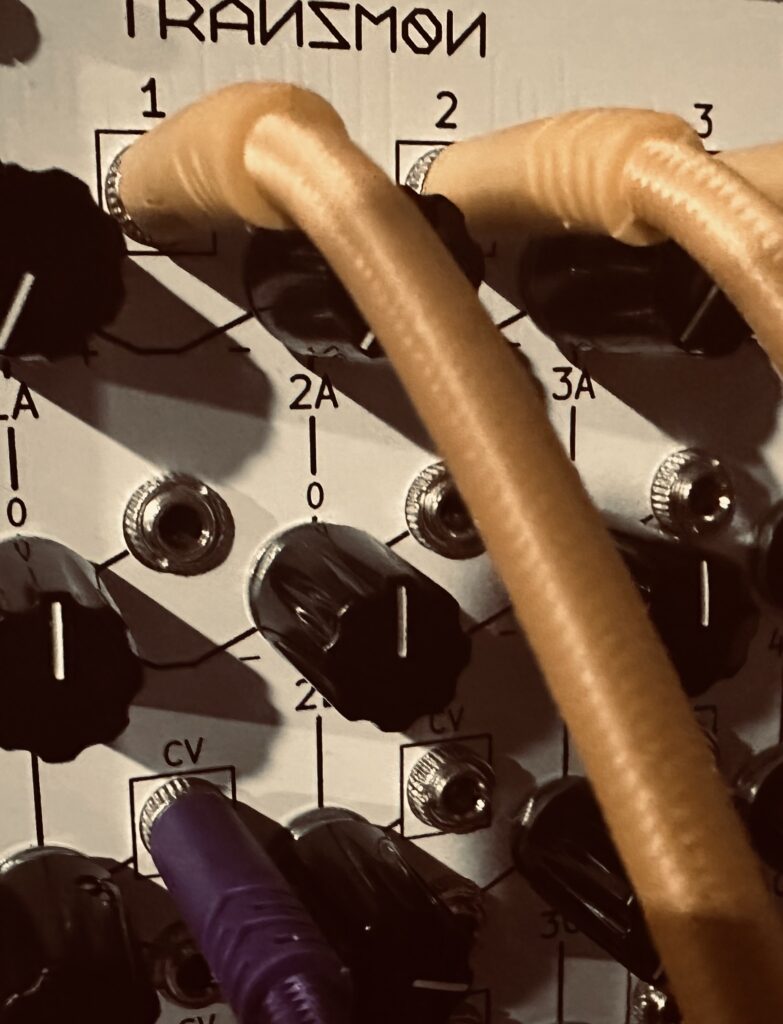
Modulation of the E370 wasn’t particularly heavy in this patch, but each oscillator’s X axis was moved around by a complex mix of CV from the Nonlinearcircuits Frisson mixed together in the Atomosynth Transmon CV controlled matrix mixer. Four randomly chosen outputs from Frisson were sent to the four inputs of the Transmon, with the other four Frisson outputs modulating four separate nodes in the mixer itself. This modulation to the E370’s X axis was at a medium slow speed and moved waves around beautifully, slowly shifting the sine wavetables.
The Atomosynth Transmon is a curious module. Nominally it’s a matrix mixer, made by a very niche maker based in Lima, Peru. But this matrix mixer has several tricks up its sleeve. The first row can be used for the attenuation or attenuversion of signals, a switch controlling which mode is active. The second row can do both, and each node has an individual output. The last two rows each have a discreet VCA input per node, also with individual outputs. If one of those individual outputs is used, it’s removed from the final mix of the row. Each node can also be used as a 12V offset voltage using jumpers on the back. The Transmon is a very powerful and flexible mixer that can be used in a myriad of ways. Most often I use it for simpler mixes, or even as individual VCAs, but this patch called for going whole-hog, mixing four chaos signals, while using four of Transmon’s individual VCAs to modulate my modulation. These new modulated modulation CV mixes create all of the tonal shifts in the E370 voice as they move the sine waves through a series of notes along the X axis of the wavetable. The pitch CV being sent was constant through the recording. I could have manually tuned each oscillator to those notes and the result would have been no different.







Although I was much more pleased with the result after changing wavetables, it wasn’t enough change. The original delay I had chosen for the E370, the Holocene Electronics Non-Linear Memory Machine, was no longer the best tool for the job. Although its inherent aliasing worked great with the original wavetable, I didn’t like it at all with the much cleaner waves I was using at the time. It created too choppy a repeat, even with some diffusion and without pitch shifting. So I switched over to the very clean Olivia Artz Modular Time Machine, which worked a treat. With a medium length delay time, notes were lengthened and it gave the overall sound a bit of thickness, even if I didn’t pay much attenuation to how I set up each tap.
With the primary voice more-or-less set, it was time to fill in the cracks. The flowing waves of the E370-plus-noise mix with its delay and some reverb were beautiful, but lonely. It was heavy on high(er) pitches, and I wanted to add a bit of body to it. In comes Panharmonium. Though it’s highly capable, I very rarely use Panharmonium as a main voice. But I use it all the time as a supplement to the primary voice as a means of reinforcement, most often shifting the pitch in one direction or another so that various frequency ranges are represented. In this patch I initially went with a two octave downward shift. It was deep, but not overpowering, in a beautiful way, though there was simply too much that wasn’t being heard at all because the frequencies were just too low, which too often caused a flutter that sounded like clipping. No good. So I compromised by going down only one octave, (introduced at 1:15), which transmogrified the audio into a warm bath. I don’t normally modulate Panharmonium, I haven’t found it needed, but for this patch I decided to use offset and attenuated versions of the Swell Physics Average output to modulate both the Center Frequency and Bandwidth, which created a slight swirl in the output which added texture.
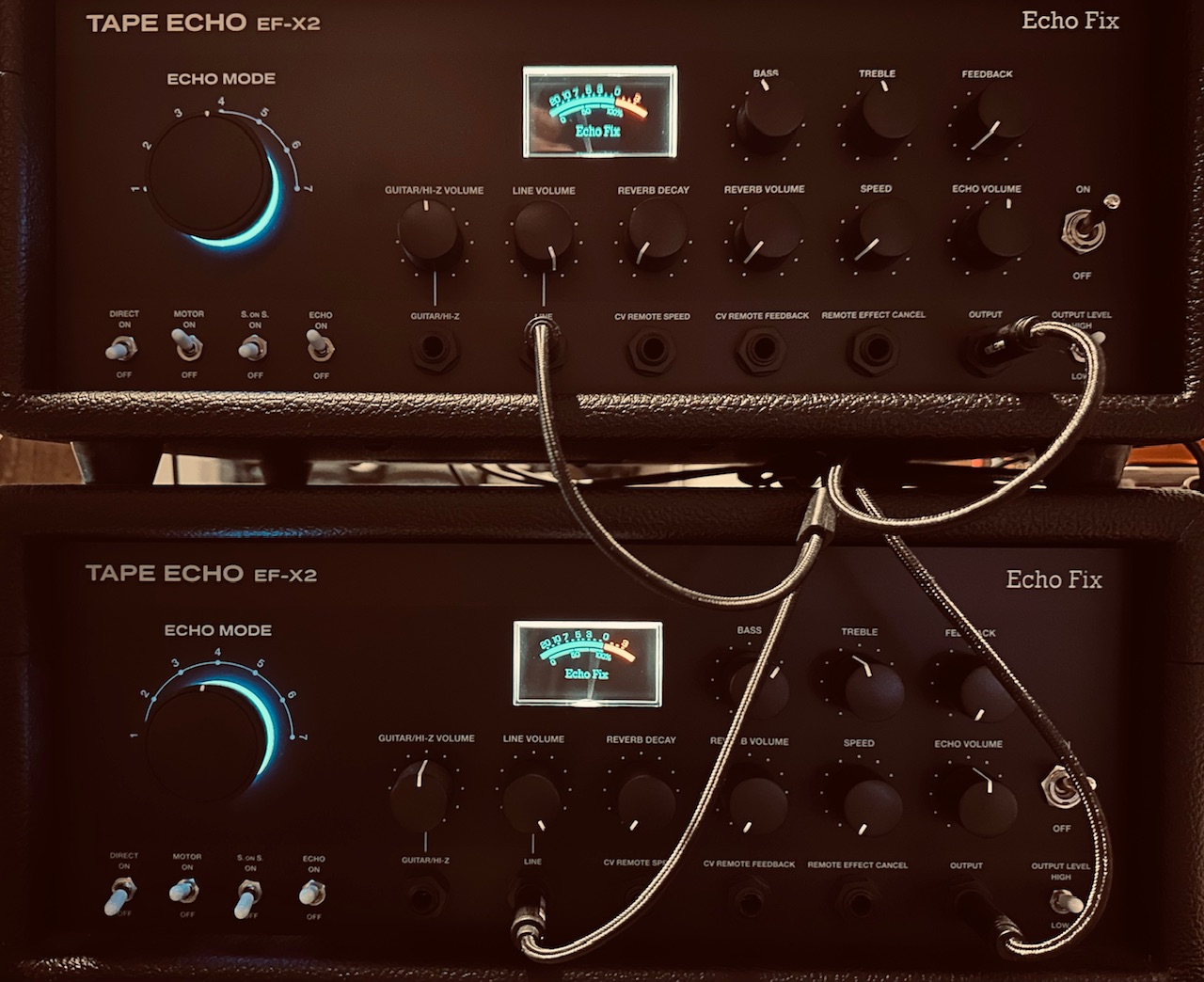
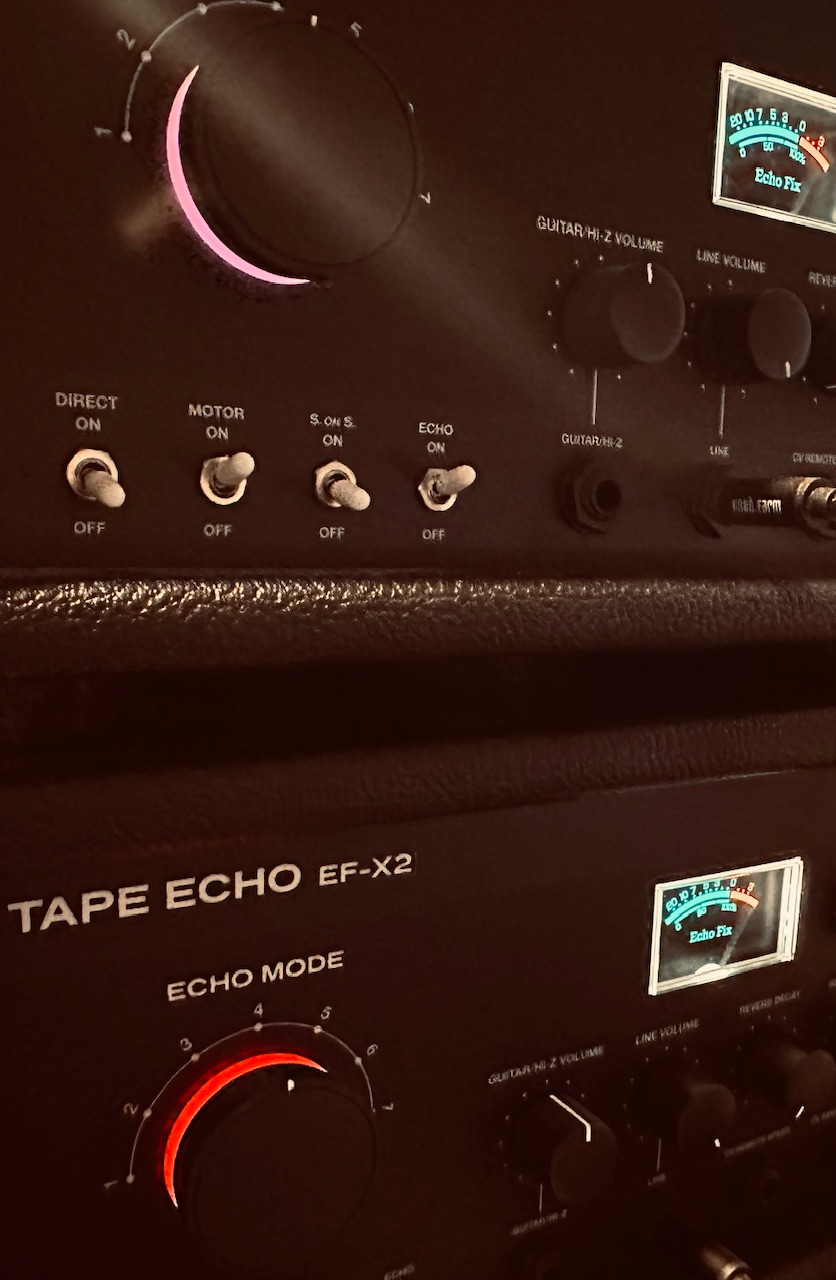
But I didn’t stop there. The Panharmonium voice was beautiful, but it needed delay for a bit of thickness of its own, so I sent its output to a pair of very slightly driven Echofix EF-X2s, with its speed lightly modulated by a triangle wave from a Frap Tools Falistri, giving it a hint of vibrato in the delay tails. The offset delays helped create a beautiful stereo image, and added a slight bit of focus.

Now that we had a beautifully flowing soundscape of waves, it was time for some ornamentation. Recently I’ve been reaching primarily for my pair of ever wonderful Pladask Elektrisk Dradd(s) when I’m looking for granular synthesis, but I knew I wanted at least one thing that Dradd cannot do: a two octave shift to create sparkles. It can do a one octave shift in Tape Mode, but not two octaves. So I turned towards the Mutable Instruments Beads (introduced at 2:30). I’ve had Beads a long time. It was one of my first modules, bought on a whim when I saw they were in stock one day. Beads can be many things from delicate to bombastic, and with this patch I wanted subtle, and Beads excels at being subtle. Like all granular processors, finding a nice sweet spot (or range) can be a challenge, but the controls are intuitive and once you find that range, Beads can produce wonders to behold. With slight modulation from Tides to Size, along with use of the attenurandomizer circuit to Time, and I had a beautiful spray of shimmering grains to follow in the wake of the E370 and Panharmonium waves. But even with this beautiful flow of waves I wanted something more. Something to use as juxtaposition. Something with more edge.


One module that I’ve criminally underused is the Frap Tools Brenso. I’ve certainly used it before, but it’s daunting, and I haven’t really put much brain power towards learning it, so I’ve tended to use its standard shaped outputs, while ignoring the gobs of waveshaping and wavefolding on the right side of the module. It’s a shame, really, but I thought that this day would be a good day to start exploring the extensive tonal options on the panel. I decided to start simple, using Sapel’s two smooth fluctuating random signals to slowly and lightly modulate both the waveshaper and wavefolder. This created an almost crackling electricity sound at times. It sputtered. It growled. It was an uneasy signal, fraught with fear while trying to exert its independence. I ran the Final output from Brenso through CUNSA, mixed with noise like the E370 waves, for some light filtering to attenuate some of the most egregious frequencies. The last time I made a patch like this I used a sequencer and pure sine waves for the epic sub bass line. It was way too loud, even if it was intentional, and repetitive. It was also pitched far too low. This time around I decided to use the same module to create the bass line, but rather than use a sequence, I used the Doboz T12 in Touch Keyboard mode and manually played the part. I wanted to time the note changes by feel rather than a clock. It’s still too loud, and still probably too low in pitch (some lessons are harder to learn than others), especially as I go up in register, but placing this very uneasy and slightly dirty wave in contrast to the smooth waves of the E370 and Co was a nice touch. Were I to record this patch again, I would definitely do a better job of controlling the level of this voice. I think the recording still sounds great, but I was certainly a bit overzealous with the volume of this voice.






For reverb I used my trusty Walrus Audio Slöer in Light mode for a choral sounding octave up shimmer. This reverb really has become my primary reverb. I only move away from it once it proves itself to not be the best tool for the job.
Improvised and recorded in one take on iPad in AUM via the Expert Sleepers ES-9.
Modules Used:
Addac System Addac508 Swell Physics
Addac System Addac814 6×6 Stereo Matrix Mixer
Synthesis Technology E370
Nonlinearcircuits Divide & Conquer
Nonlinearcircuits Frisson
Atomosynth Transmon
Intellijel Amps
Intellijel Quad VCA
Olivia Artz Modular Time Machine
Frap Tools Sapel
Frap Tools Brenso
Frap Tools CUNSA
Frap Tools 333
Frap Tools Falistri
Doboz T12
Rossum Electro-Music Panharmonium
Vostok Instruments Asset
Mutable Instruments Beads
Mutable Instruments Tides v2
ST Modular SVCA
Knob Farm Ferry
Outboard Gear Used:
Walrus Audio Slöer
Noisy Fruits Lab Lemon
Echofix EF-X2 (no idea why this is no longer on their website)
- Technically I had my iPad, which, from my Jamuary experience, is more than enough music making machine, but I simply wasn’t inspired by anything on it at the time. ↩︎